Ultrabroadband and band-selective thermal meta-emitters by machine learning
Thermal nanophotonics enables fundamental breakthroughs across technological applications from energy technology to information processing. However, it remains a considerable challenge to develop a general design methodology for tailoring high-performance nanophotonic emitters with ultrabroadband control and precise band selectivity, as they are constrained by predefined geometries and materials, local optimisation traps and traditional algorithms. A research team led by Professor Qiu Chengwei, Chief Principal Investigator from the Energy and Environmental Nanotech Research Platform of NUSRI Suzhou, in collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University and University of Texas at Austin, has proposed an unconventional machine learning-based paradigm that can design a multitude of ultrabroadband and band-selective thermal meta-emitters by realising multiparameter optimisation with sparse data that encompasses three-dimensional structural complexity and material diversity. The researchers also provided a generalisable framework for fabricating three-dimensional nanophotonic materials, which facilitates global optimisation through expanded geometric freedom and dimensionality and a comprehensive materials database. The results were published in the journal Nature.
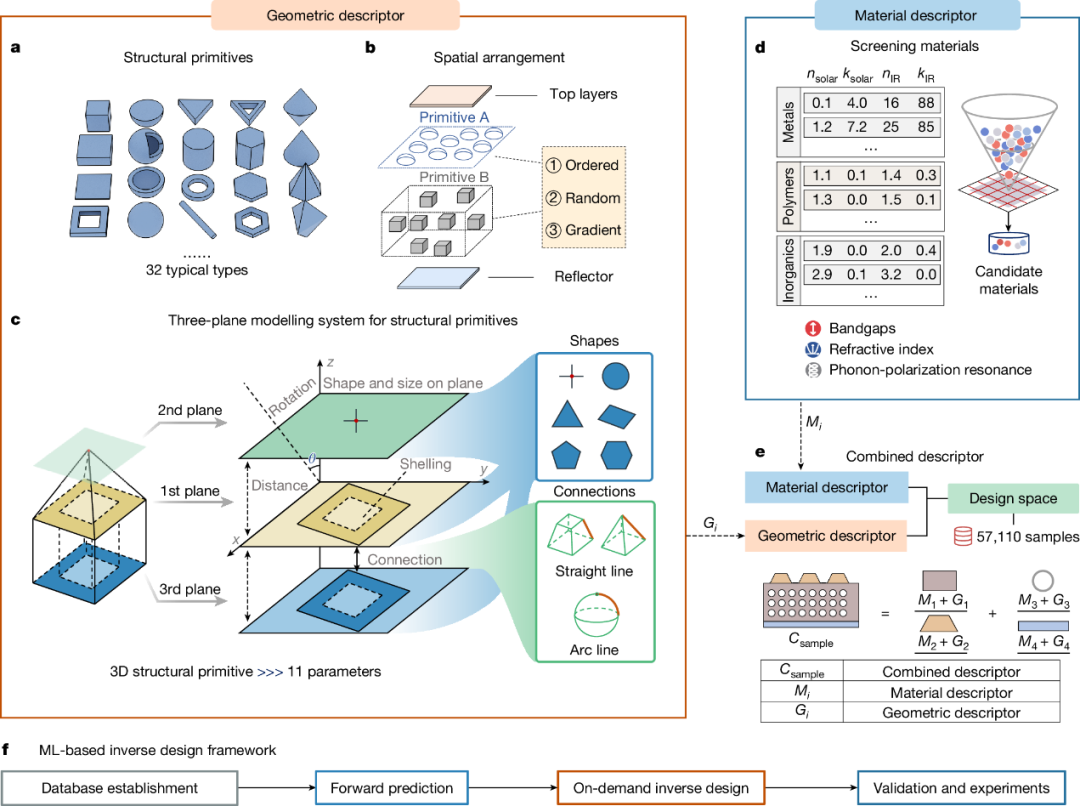
△ML-based inverse design process and descriptors